Brand Reinvention
-
The Art of Brand Reinvention: Crafting a New Identity in the Age of Consumer Evolution
-
The corporate landscape is in a constant state of flux, its volatile terrain shaped by the forces of technology, socio-economic factors, and changing consumer behaviours. In such an environment, businesses can rarely afford to remain static, particularly when it comes to their most precious asset: their brand. Thus, brand reinvention emerges not just as a survival tactic but also as an approach to seize growth opportunities. The masters of this game are companies like Apple, McDonald’s, and Lego, each having undertaken a series of brand transformations to achieve astounding success.
As the axiom goes, change is the only constant. This statement stands unequivocally true in the corporate world, where companies must adapt or face obsolescence. Nevertheless, the process of brand reinvention is far from simple; it involves substantial risk and requires a deep understanding of the brand, its customers, and the market at large.
-
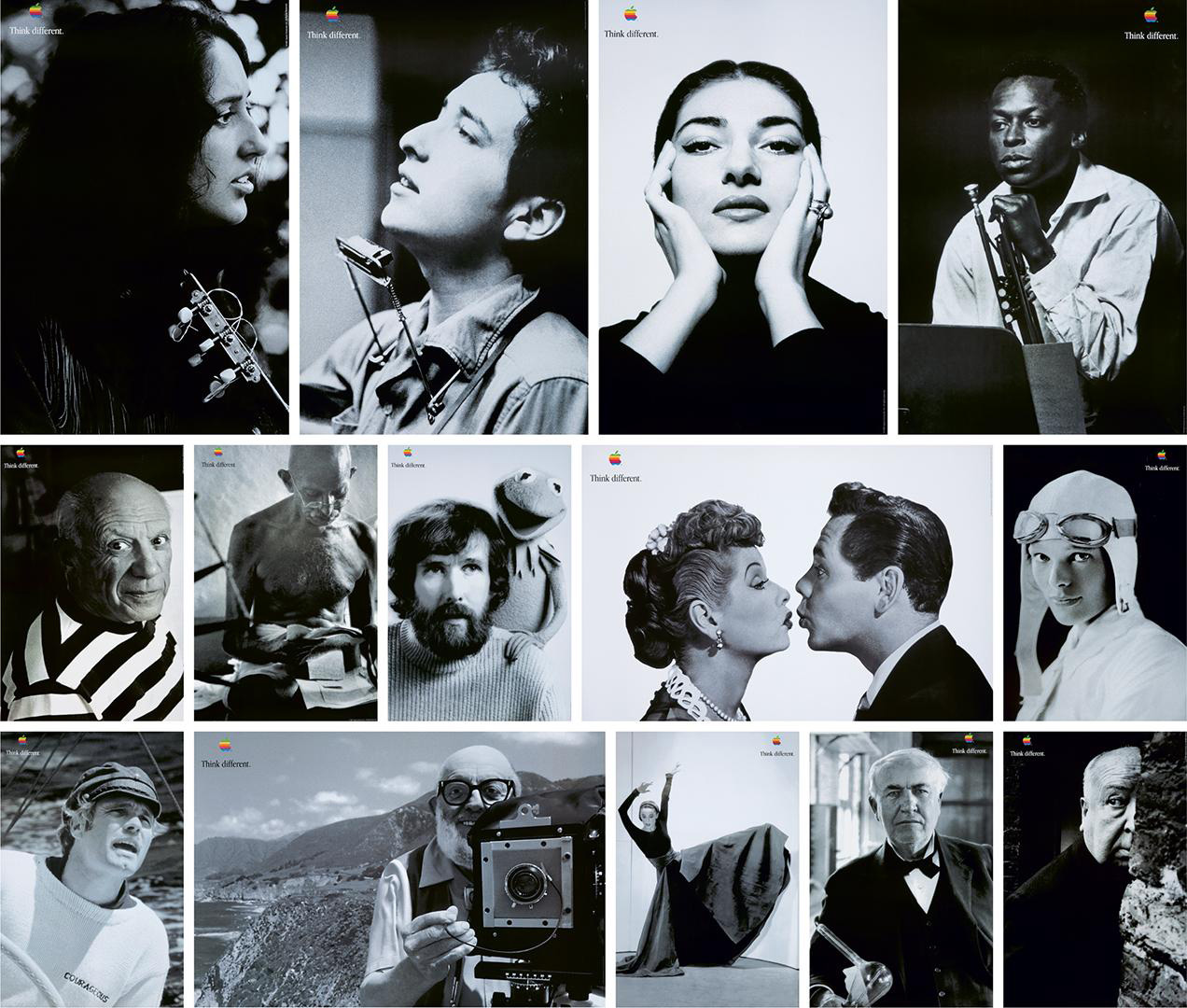

Apple Think Different 1997 — 1998
-
The Crucial Need for Reinvention
To understand brand reinvention, one must first recognise its necessity. Consumer preferences shift like quicksand, technology advancements redraw industry borders, and competition increases as new players enter the field. Furthermore, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has amplified these challenges, prompting an urgent need for businesses to reassess their brand value propositions.
The hallmark of successful reinvention lies in the ability of a brand to evolve in step with its audience. This doesn’t mean pandering to every passing trend, but rather recognising fundamental shifts in consumer values and behaviour. A brand that remains unaltered for decades may eventually lose its relevance, or worse, become a symbol of a bygone era. On the other hand, brands that successfully reinvent themselves can solidify their existing customer base and attract new demographics, ultimately strengthening their market position.
-
Case Studies in Successful Brand Reinvention
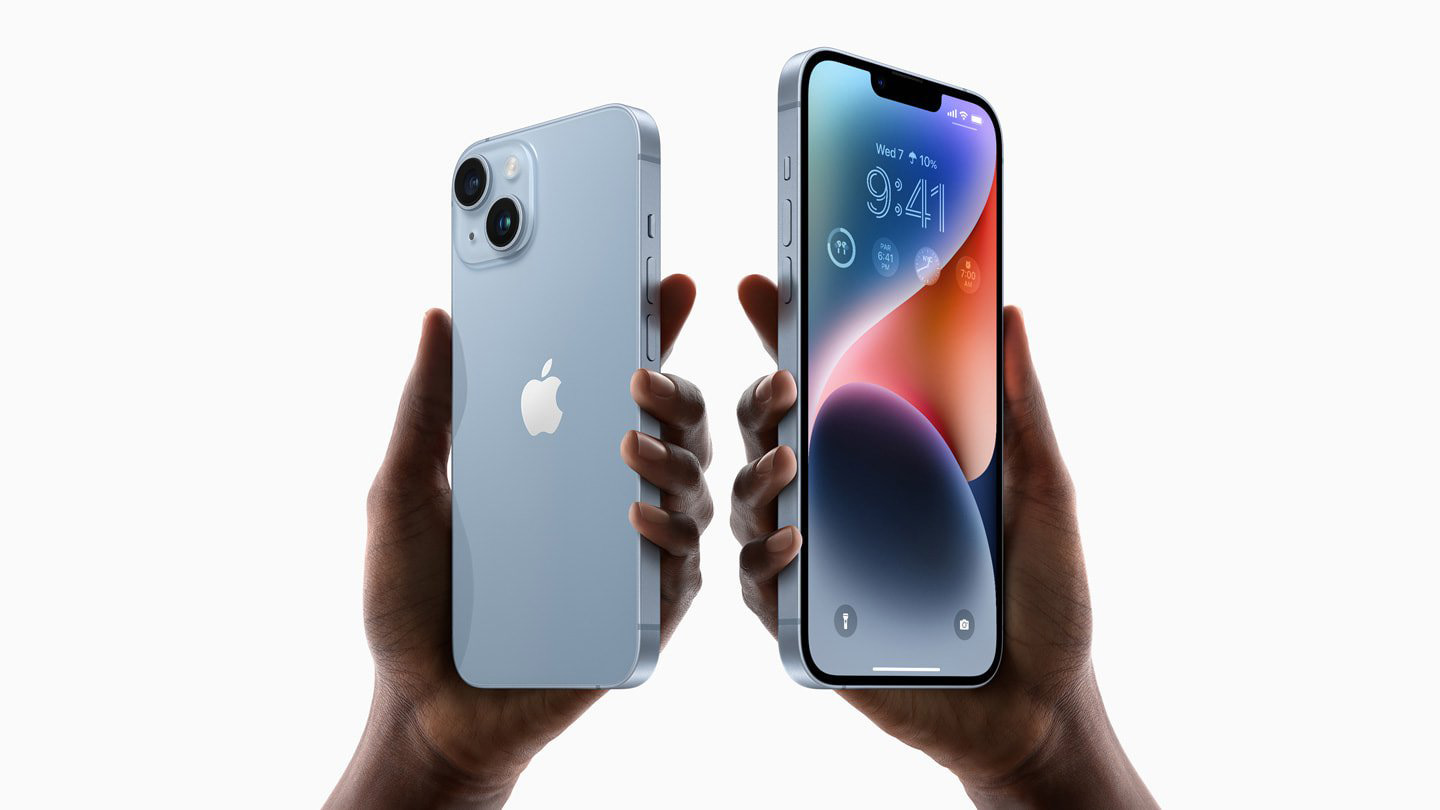

Take Apple, for example. Before the turn of the millennium, Apple was essentially a computer company struggling with sales. With Steve Jobs’ return, Apple underwent a dramatic brand reinvention, expanding beyond personal computers to launch products like the iPod, iPhone, and iPad. This shift not only transformed Apple’s brand image from a niche computer manufacturer to a lifestyle technology innovator, but also catalysed its journey to become one of the most valuable companies globally.
In a very different industry, McDonald’s faced declining sales and a damaged reputation in the early 2000s, as the fast-food giant was being heavily criticised for contributing to global obesity. McDonald’s responded by initiating a brand reinvention that incorporated healthier options in their menu and fostered transparency about nutritional information. This strategy allowed McDonald’s to regain the trust of its customers and reposition itself in the market.
-
Crafting a Successful Reinvention Strategy
Despite the inherent risks, the process of brand reinvention can be navigated successfully with a well-thought-out strategy. It requires businesses to reassess their core values, revisit their target demographics, and reevaluate their competition.
The journey typically starts with introspection: what is the essence of the brand? Does it still resonate with its audience? Is it adaptable to contemporary needs? The next step involves identifying the desired future state of the brand, often influenced by market research, competitor analysis, and a deep understanding of current and potential customers.
The execution phase is where the transformation comes to life, manifesting in various ways including product diversification, a shift in communication strategy, or a complete visual rebranding. Regardless of the specifics, successful execution hinges on aligning the new brand identity with the company’s strategic objectives and ensuring consistency across all customer touchpoints.

A crucial factor often overlooked in the brand reinvention process is internal alignment. Employees, the backbone of any organisation, need to be involved in the reinvention process, understanding, and endorsing the new brand vision. Any disconnect between a company’s internal culture and its external brand image can lead to a lack of authenticity that savvy consumers are quick to spot.
-

-
The Risks of Reinvention
As with any strategic decision, brand reinvention is not without its risks. Missteps can lead to customer alienation, market confusion, and a damaged reputation. Yet, the rewards of a successful reinvention far outweigh the potential pitfalls. In an era where the consumer is king, businesses that learn to adapt, evolve, and reinvent their brand identity are the ones poised for enduring success.
Reinvention is not about altering the fundamental DNA of a brand. Instead, it’s about understanding the evolving market, identifying the brand’s role in this new landscape, and strategically steering the brand towards a future that aligns with both its core values and the shifting needs of consumers. As businesses across the globe grapple with change, brand reinvention emerges as a potent tool to stay relevant, competitive, and prosperous in the corporate landscape of the 21st century.